There’s no denying that AI is outpacing the development of the laws that regulate it, and that’s worrying from a cybersecurity perspective. Gaining additional access and control, and operational capabilities, the AI engages with more tools and data. Here comes the model context protocol MCP.
Organizations face a single, fundamental dilemma: how do we ensure that the AI carries out only the tasks it is intended to accomplish?
Introduction
For the last 1-2 years, there have been security analysts, developers, and regulators warning of the risk of uncontrolled AI integrations. Shadow tools, unpredictable model behaviors, and the absence of uniform access control have meant a multi-pronged risk. What we needed was a solution that would impose order, consistency, and transparency on how AI engages with other systems.
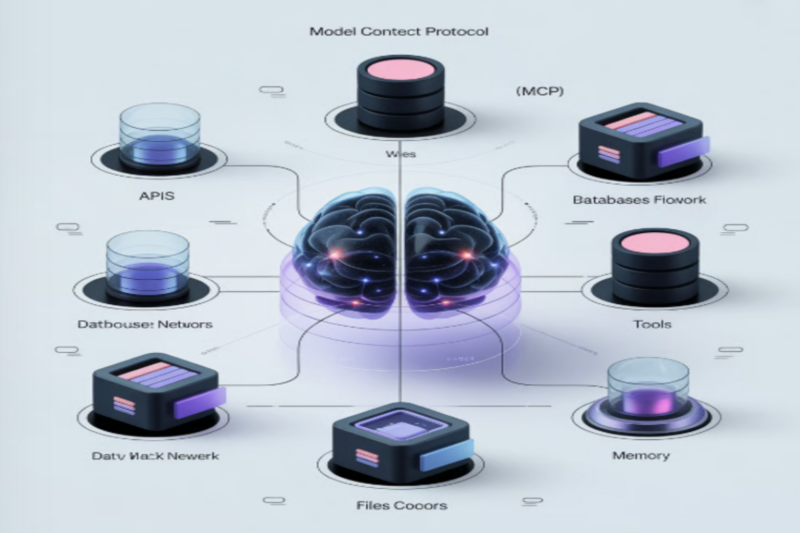
This is the opportunity that the Model Context Protocol (MCP) has been designed to represent: the growing backbone of integrative AI systems. Model Context Protocol is aimed at solving the industry’s outstanding dilemma: providing AI the ability to access a wider outer context while still maintaining the access control boundaries of security, privacy, and control.
What Is Model Context Protocol?

Let’s understand what is an MCP server. MCP is an open, standardized framework that addresses security concerns regarding how artificial intelligence (AI) models interact with external tools, data, and systems. It was developed to curb the messy ecosystem of AI and ensure that every interaction between an AI system and a connected resource runs according to clear rules that are controlled and auditable.
MCP protocol fixes an industry problem. AI systems need to fetch data, take action or use business tools. But when there is no common protocol, things are broken, risky and hard to govern. MCP enables AI models and software systems to speak a common language that can be reliably understood in a secure way.
In simpler terms, MCP acts as a bridge with guardrails. The system allows an AI to request a function, evaluates if it is permitted, and only then provides the AI access while logging and making every process transparent. It will not allow the AI to overreach, access data it should not have, and act out of scope.
As a result, developers, enterprises, and security teams are rapidly embracing MCP as the go-to building block for secure AI deployment.
Implement MCP Services in Security!
Looking to implement Model Context Protocol the right way? Let’s turn your AI ideas into production-ready solutions.
Why MCP Matters in Cybersecurity

As AI programs become part of business workflows, they are handling sensitive data, interacting with internal systems, and taking actions normally done by people.
If there is no common security layer, then these interactions between the generative AI and the enterprise systems can lead to new security weaknesses. This is where the Model Context Protocol becomes critical.
MCP enables AIs to use only approved tools and datasets within the limits of their permissions. It is a big step forward for cybersecurity as AI going off the rails or crossing lines due to vague instructions or compromised prompts is an up-and-coming threat.
The protocol also enforces full visibility and auditing. All actions performed by an AI via MCP are recorded, enabling the security team to track behaviours and anomalies while ensuring regulatory compliance.
MCP also diminishes the growing risk of shadow AI, which refers to the unauthorized integration of AI tools into corporate environments. By allowing only approved tools to connect to the organization’s systems, MCP acts as a gatekeeper for the organization.
What the AI-powered security technology of today really needs is predictability, manageability, and a framework that is zero-trust by design.
Get 20% off on your first hosting purchase. Provide everything you need to create your website.
How Model Context Protocol Works
The Model Context Protocol functions through a structured, permission-based architecture that governs how an AI system interacts with external tools and data sources. Instead of giving AI free access, MCP creates a controlled, auditable pathway ensuring every action is intentional, validated, and secure.
Below is a clear breakdown of how MCP works inside a real system:
The Client–Server Model
MCP operates on a simple but powerful architecture:
- Client: The AI model or AI-powered application requesting access.
- Server: The system, database, or tool that the AI wants to interact with (e.g., file storage, analytics engine, CRM data, security logs).
Both sides communicate using the MCP standard, ensuring predictable, universal compatibility across platforms.
Declaring Capabilities
Before the AI can do anything, the server advertises its capabilities, listing specific actions it can perform.
Examples:
- “Read customer data.”
- “Fetch log files”
- “Execute search queries.”
- “Write updates to a record.”
This step defines the boundaries. If a capability isn’t listed, the AI cannot access it.
AI Requests an Action
Let’s understand what is MCP in AI. When the AI wants to perform a task, it sends a structured request through MCP.
This request includes:
- The capability it wants to use
- The purpose
- Any input data
- Required parameters
The request format is standardized, eliminating ambiguity that can lead to hallucinations or unsafe actions.
Authorization & Validation
The server receives the request and performs checks:
- Is this AI authenticated?
- Is it allowed to use this capability?
- Is the request safe, complete, and within policy limits?
Only after passing these checks does the server allow the action.
MCP Can Trigger More Tool Calls if Needed
If the model realizes the task needs more information, it can automatically call another MCP tool. For example:
- If it asks for “user profile” but also needs “saved projects,” it will trigger a second tool call
- If the previous data was insufficient, it can request additional fields
This enables autonomous, multi-step workflows without coding multiple prompts.
Real-World Use Cases
The following are the real-world use cases described below:
Threat Analysis Tools Using MCP to Access Logs Safely
Modern SOC platforms (like Splunk, Elastic, or Sentinel) can integrate MCP to let AI analyze logs without directly exposing raw sensitive data.
How It Works:
- MCP creates controlled “log access tools” that expose only specific fields (timestamp, event type, severity).
- The AI can query error patterns, detect anomalies, or flag suspicious authentication attempts.
- The model never sees full, unfiltered PII, device IDs, or system internals.
Industry Impact:
- Reduces risk of sensitive log leaks.
- Enables near-real-time automated incident detection and classification.
- Helps SOC teams handle 5× more alerts with less fatigue.
This is particularly useful in financial institutions where log data contains confidential identifiers.
Pentesting AIs Interacting with Vulnerability Scanners Securely
Pen-testing agents can now run automated tests without being given unrestricted access to tools like Nessus, OpenVAS, Burp Suite, or Nmap.
How MCP Enables This:
- Pentest AI gets controlled access to vulnerability scanning results through MCP tools.
- The AI cannot trigger unauthorized network scans.
- It only retrieves structured findings: CVSS score, affected asset, exploit details, and remediation guidance.
Practical Scenario:
A red-team AI asks the scanner tool: “List all assets with high-severity CVEs discovered this week.” The MCP endpoint returns the sanitized output, not the full system topology or network map.
Benefits:
- Limits the exposure of sensitive architectural details.
- Prevents rogue AI actions.
- Supports automated reporting while maintaining strict access boundaries.
Limitations and Challenges
MCP is still new; large-scale enterprise deployments are developing. Many AI platforms and internal tools don’t support MCP natively integration takes time.
Teams need developers to set up MCP servers, define tools, create permission rules, and manage updates. Admins, SOC analysts, and engineers must learn how MCP permissions and tool-scopes work.
The Future of MCP in Enterprise
MCP is poised to become one of the most important standards in AI security. Many experts expect it to gain the same relevance that OAuth achieved for authentication. As governments work on AI governance laws, MCP provides exactly what regulators want: transparent, auditable, restricted AI access to corporate data.
Over the next few years, MCP is expected to become:
- a global standard for controlling enterprise AI agents
- a mandatory requirement in regulated sectors (finance, healthcare, government)
- a core component of AI governance compliance in the US and EU
- a tool auditors will rely on to review AI behaviors and tool interactions
As AI agents become more autonomous, MCP offers the safety layer needed to keep them predictable, governable, and aligned with security rules.
Conclusion
As AI integrates deeper into business workflows, the real challenge isn’t capability, it’s control. Model Context Protocol gives companies exactly that: a structured, transparent, and safe way to manage what AI can access and what it can do.
As cyber threats grow more advanced, relying on traditional security measures alone puts businesses at risk. The right AI-powered tools can help you detect threats faster, respond smarter, and protect critical data proactively.
FAQ
What is Model Context Protocol (MCP)?
Model Context Protocol is a standardized way for AI models to access, share, and manage external context such as tools, files, APIs, and memory in a secure and structured manner.
Why is MCP important for AI applications?
MCP ensures consistent context handling across AI systems, making integrations more reliable, scalable, and secure while reducing custom glue code.
How does MCP improve AI security?
MCP enforces controlled access to context sources, limiting data exposure and reducing the risk of unauthorized access or prompt injection attacks.
Who should use Model Context Protocol?
MCP is ideal for AI developers, SaaS companies, enterprises, and teams building AI agents that need structured access to tools, data, and workflows.
Is MCP only for large AI systems?
No. MCP can be used by startups and small teams as well, especially those building modular AI applications that require clean, reusable integrations.